When should you see a doctor?
You should consult a doctor if:
- you have persistent pain in the thumb area, despite rest
- You notice restrictions in everyday life (problems with gripping, no longer able to turn)
- Advanced joint destruction is suspected
Imagine waking up in the middle of the night because your hand is tingling or numb. Perhaps you feel like you can no longer move your fingers properly – as if they have fallen asleep. These symptoms are typical signs of carpal tunnel syndrome, one of the most common so-called constriction syndromes of the upper extremity. But what exactly is behind it and how can the problem be treated effectively? Here you can find out everything about the causes, symptoms and the latest treatment options – from gentle measures to targeted surgical interventions.
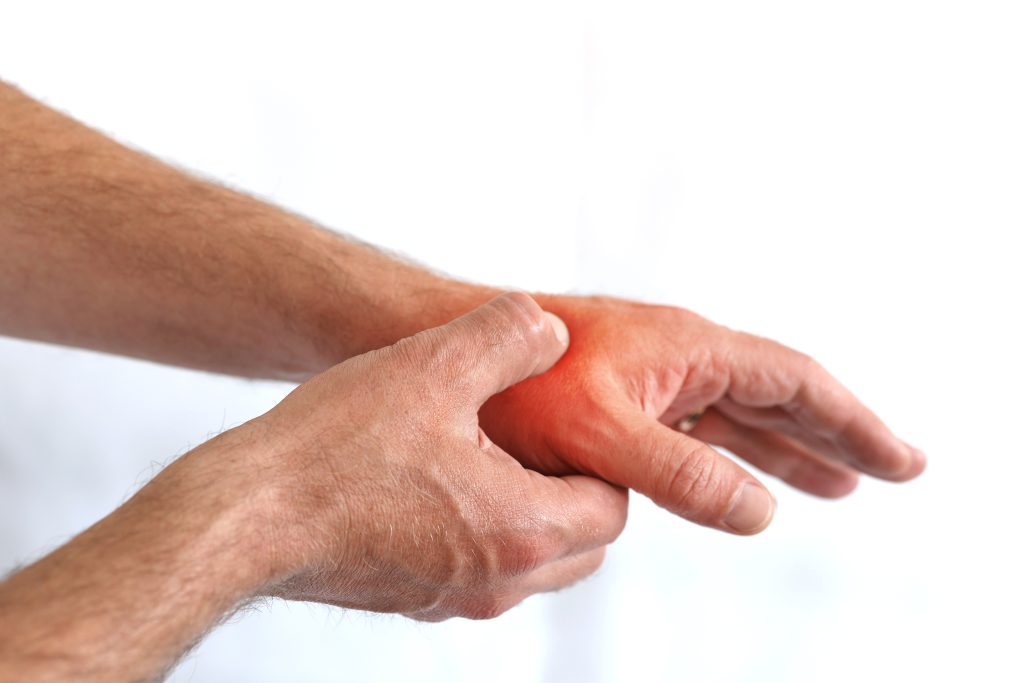
Rhizarthrosis affects the thumb saddle joint, which wears out. This serves as a connection between the large polygonal bone (a carpal bone) and the first metacarpal bone. The metacarpal bone is then connected to the first two finger bones of the thumb. Rhizarthrosis is the most common form of joint wear and tear (osteoarthritis) in the hand.
The mobility of the thumb decreases due to wear and tear in the joint, which considerably restricts hand function. As with all osteoarthritis, there are four stages that need to be distinguished:
Rhizarthrosis is caused by increasing wear and tear of the joint cartilage, which serves as a buffer between the bones. The cause of rhizarthrosis can be divided into primary and secondary rhizarthrosis.
Primary rhizarthrosis is unexplained in most cases. However, women over the age of 50 are most commonly affected, and hormonal changes during the menopause can be a trigger. However, incorrect and excessive strain are also a cause of rhizarthrosis.
Secondary rhizarthrosis is caused by a poorly healed injury or constant overloading can lead to permanent damage to the thumb saddle joint. If this injury heals poorly, wear and tear can occur and osteoarthritis of the thumb saddle joint develops.
Rhizarthrosis causes particular pain during rotational movements and gripping.
Rhizarthrosis causes particular pain during rotational movements and gripping.
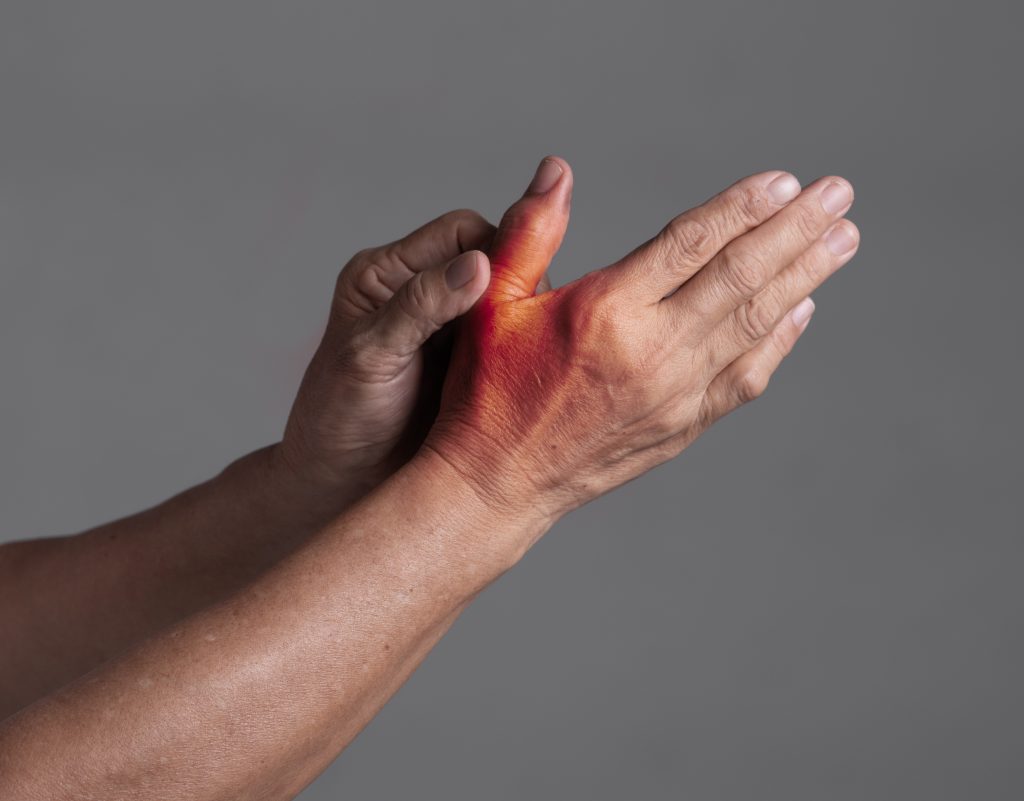
The diagnosis of rhizarthrosis is determined as follows:
You should consult a doctor if:
Whether conservative or surgical treatment is chosen depends on the degree of wear.
On the one hand, patients are prescribed a splint. This supports and relieves the thumb saddle joint. There are several different types: Splints made of plastic or metal, but also leather, which also supports the wrist.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are usually prescribed as painkillers, which are either applied directly to the thumb as an ointment or taken as tablets.
If the thumb saddle joint becomes inflamed, the doctor can administer a cortisone injection directly into the joint. These have an anti-inflammatory effect, but can only be administered for a short time.
Ergo-therapy, electrotherapy and radiotherapy are also helpful for rhizarthrosis.
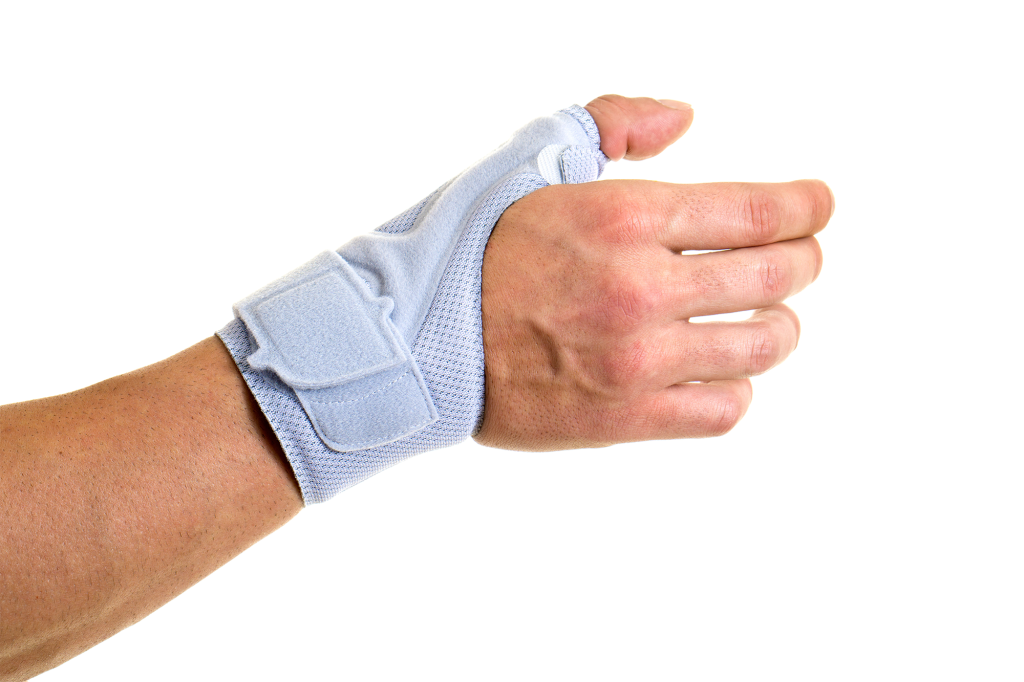
In advanced stages, conservative therapies usually no longer help. Surgical treatment is therefore arranged depending on the stage.
When operating on rhizarthrosis, the doctor chooses the appropriate procedure for the individual patient. The most common procedure is trapezius resection – a small carpal bone (os trapezium) is removed and the gap stabilized with a tendon strip. Alternatively, the joint can be stiffened (arthrodesis), an artificial joint can be inserted or pain-conducting nerve branches can be cut in order to alleviate the symptoms.
Rhizarthrosis can noticeably restrict everyday life, but does not have to be a reason to lose independence. Many sufferers learn to cope well with the disease, especially if it is treated early and everyday life is adapted accordingly.
Working with rhizarthrosis is still possible in many cases, especially with mild to moderate symptoms. It is important to load the wrists as evenly as possible, avoid monotonous or very force-intensive movements and use aids if necessary.
There are also many ways to relieve the hand in everyday life – for example with bottle openers with leverage, non-slip pads or special kitchen aids. Heat, relaxing hand baths and targeted movement exercises can also alleviate symptoms.
Rhizarthrosis cannot be completely prevented, as it often occurs due to age or predisposition. Nevertheless, the following measures help to keep the joints healthy for as long as possible:
Priv.-Doz. Dr. Sebastian Farr is a specialist in orthopaedics and hand surgery with many years of experience as a senior physician at the Orthopaedic Hospital Speising. At his surgery in the 1st district, he offers comprehensive advice and individual treatment options for diseases and injuries of the hand and upper extremities. From diagnosis to treatment and aftercare, Dr. Farr will accompany you personally and attaches great importance to precise diagnostics and targeted treatment. The aim is to restore hand function in the best possible way and to alleviate pain in the long term.
Arrange a consultation today by e-mail, online or by telephone and let Priv.-Doz. Dr. Sebastian Farr personally about your treatment options – for more comfort, quality of life and an active life!

Initially, rhizarthrosis often manifests itself as slight pain when gripping or turning, for example when opening bottles or writing. The symptoms often disappear again at rest.
A complete cure is not possible as it is a matter of wear and tear. However, with targeted treatment, the symptoms can be significantly alleviated and progression slowed down.
Yes, sports that are easy on the joints such as swimming, cycling or special hand exercises are recommended. It is important to avoid overloading.
Heat applications, ergonomic aids, targeted exercises and avoiding one-sided strain help to relieve the joints and maintain mobility.
No. Many patients cope well with conservative measures. Surgery is usually only necessary at an advanced stage if the pain is severe and permanently debilitating.
In most cases, yes – depending on the job. With ergonomic adjustments, breaks and, if necessary, a workplace evaluation, many occupational requirements can still be mastered.
Use aids, avoid overloading and pay attention to ergonomic handling during everyday activities.